Recognizing the Innovation Behind the Galvanometer Scanner for Accurate Readings
Recognizing the Innovation Behind the Galvanometer Scanner for Accurate Readings
Blog Article
Exactly How a Galvanometer Scanner Boosts Efficiency in Laser Scanning Technologies
The assimilation of galvanometer scanners in laser scanning modern technologies stands for a critical improvement in precision engineering. By assisting in rapid and precise changes of laser light beam instructions, these devices substantially enhance operational performance across various applications, from clinical imaging to industrial inscription. The underlying electro-magnetic systems, paired with advanced responses systems, make sure real-time control and enhanced accuracy. As industries significantly demand greater performance requirements, the question emerges: what future technologies might better raise the capabilities of galvanometer scanners in this developing landscape?
Comprehending Galvanometer Scanners
A galvanometer scanner is an advanced tool that leverages electro-magnetic concepts to achieve specific angular movement of mirrors or other reflective surfaces. These scanners operate with the communication of an electric present and an electromagnetic field, allowing fast and precise positioning. This modern technology is vital in applications calling for high-speed scanning, such as laser engraving, optical interaction, and clinical imaging.

Galvanometer scanners are often identified by their fast feedback times and high angular resolution, making them ideal for applications that require rapid movements and accurate placing. Their dependability and efficiency make them a crucial component in modern-day laser scanning modern technologies, adding substantially to developments in various fields, consisting of manufacturing, health care, and telecommunications.
Mechanism of Laser Light Beam Control
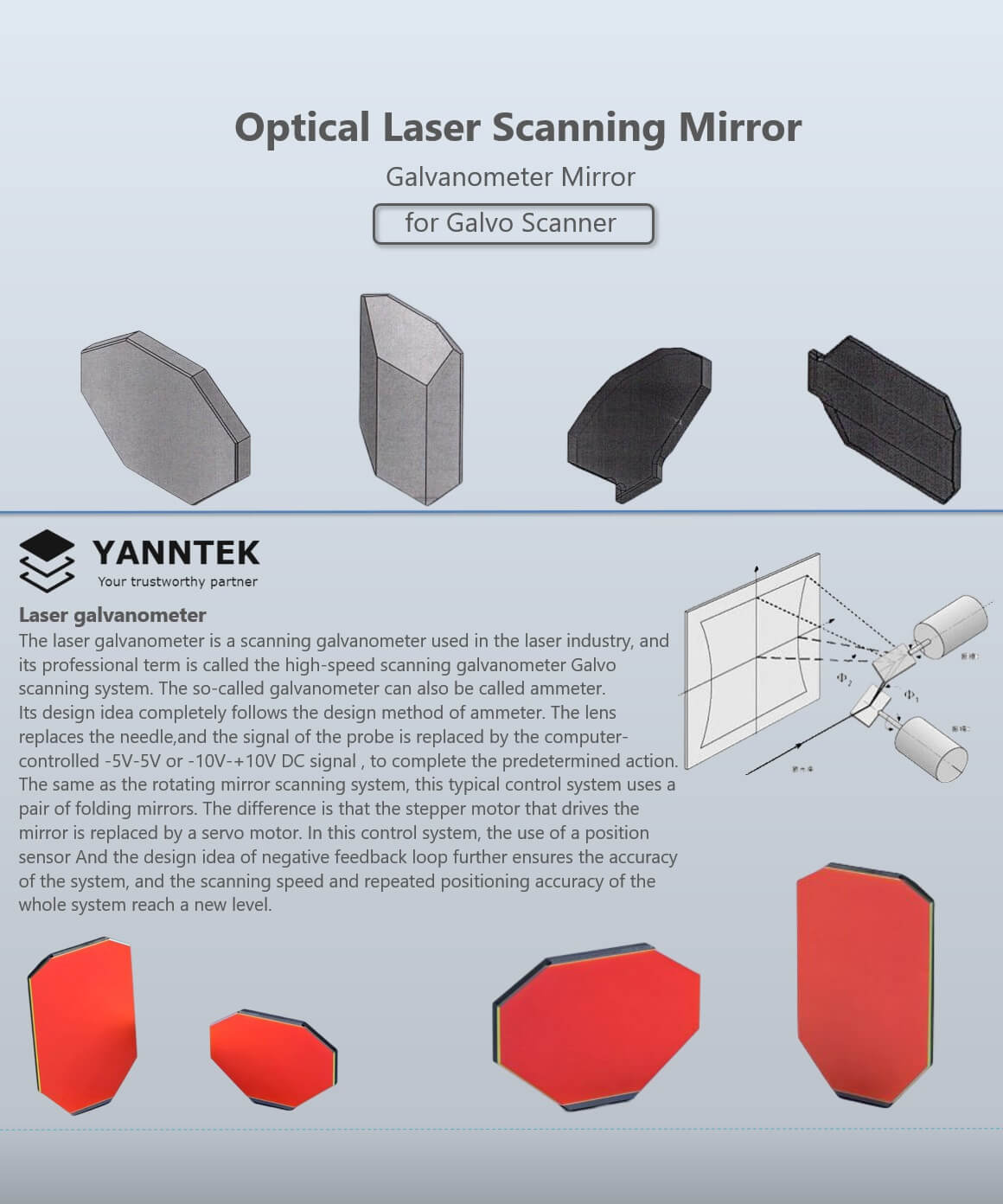
The control system counts on closed-loop feedback systems that continuously keep track of the beam's position. The signals from optical sensors supply real-time information to the control system, permitting fast changes to keep accuracy. This is important in applications where also small deviations can compromise the quality of the scan or etching.
Additionally, the galvanometer's response time is paramount; high-speed motors enable quick motions, making sure that the laser beam of light can rapidly map complex patterns or carry out intricate operations. The assimilation of electronic signal processing further boosts the responsiveness and accuracy of the galvanometer scanner. On the whole, the device of laser beam control through galvanometer scanners exhibits the blend of innovative engineering and innovation, yielding high-performance outcomes in laser scanning applications.
Benefits of Improved Accuracy
Boosted accuracy in laser scanning modern technologies supplies substantial advantages throughout numerous applications, from industrial production to medical treatments. The assimilation of galvanometer scanners permits very precise beam positioning, which is critical for jobs requiring precise detail. This boosted precision makes certain that the laser can target particular locations with very little inconsistency, causing remarkable high quality end results.
In commercial contexts, exact laser scanning navigate to these guys leads to enhanced product consistency and lowered product waste. Parts produced with high precision are less most likely to require rework, consequently enhancing efficiency and minimizing operational expenses. In clinical applications, the precision of laser procedures can considerably affect individual end results. As an example, in laser surgical procedure, specific targeting minimizes damage to bordering tissues, resulting in quicker healing times and less complications.
Moreover, improved precision helps with advanced applications such as 3D imaging and microfabrication, where even minute inaccuracies can result in considerable errors. By offering reputable and repeatable laser positioning, galvanometer scanners add to the general effectiveness and efficiency of laser systems. In summary, the benefits of improved precision not only improve operational efficiency however likewise raise the requirements of quality and security in original site various sectors.
Applications in Various Industries
The flexibility of galvanometer scanners in laser scanning modern technologies expands throughout several markets, each gaining from the precision they provide. In the clinical area, these scanners are pivotal in applications such as laser surgical procedure and imaging, enabling highly accurate targeting of tissues while minimizing damages to surrounding locations - galvanometer scanner. Their quick action and fine resolution are essential in creating high-grade outcomes
In the manufacturing field, galvanometer scanners improve processes like laser engraving and cutting. Their capability to rapidly route laser beams onto surfaces makes it possible for effective assembly line, improving rate and accuracy in developing detailed designs or elements.
The vehicle market also takes advantage of galvanometer modern technology for top quality control and assessments (galvanometer scanner). By using high-speed scanning, makers can find problems in assemblies or products, guaranteeing that products satisfy rigid standards
In addition, in the entertainment sector, galvanometer scanners are employed in laser light shows and screens, supplying dynamic aesthetic experiences website link with accurate control over laser motions.
Future Fads in Laser Scanning
Arising modern technologies are poised to reinvent the landscape of laser scanning, with galvanometer scanners at the forefront of this change. As markets increasingly demand precision and performance, the evolution of galvanometer technology will drive considerable improvements in laser scanning applications.
Future patterns indicate a growing combination of expert system and device learning algorithms, which will enhance data refining capacities and automate decision-making in real-time. This harmony will certainly permit for a lot more sophisticated analysis of scanned data, bring about enhanced accuracy in applications such as 3D modeling and self-governing navigating.
Additionally, the miniaturization of parts and the growth of advanced products will certainly contribute to lighter, more mobile laser scanning systems. This transportability will certainly expand the reach of laser scanning modern technologies right into previously unattainable atmospheres, such as remote terrain and intricate building rooms.
The surge of enhanced fact (AR) and digital truth (VR) applications will certainly additionally form the future of laser scanning. By incorporating galvanometer scanners with AR and VR, customers will gain from immersive experiences that improve visualization and job planning.
Final Thought
To conclude, galvanometer scanners play a critical duty in maximizing laser scanning innovations through their precise control of light beam direction and quick angular changes. The assimilation of innovative comments systems and optical sensing units significantly improves functional rate and precision, resulting in boosted outcomes in applications such as laser inscription and clinical imaging. As industries increasingly adopt these modern technologies, the ongoing developments in galvanometer scanner layouts are anticipated to additional elevate performance requirements and broaden application possibilities.
The integration of galvanometer scanners in laser scanning modern technologies represents a critical development in accuracy design. On the whole, the system of laser beam control with galvanometer scanners exemplifies the blend of sophisticated engineering and innovation, yielding high-performance outcomes in laser scanning applications.
By providing repeatable and trusted laser positioning, galvanometer scanners add to the total effectiveness and effectiveness of laser systems.The versatility of galvanometer scanners in laser scanning innovations expands across multiple sectors, each benefiting from the precision they supply.In conclusion, galvanometer scanners play a crucial role in maximizing laser scanning technologies with their exact control of beam direction and fast angular adjustments.
Report this page